What is Blockchain? Everything about Blockchain Technology in Simple Language

Cryptocurrency technology has gained considerable attention in recent years. If you are familiar with the cryptocurrency market and cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, you have probably heard of Blockchain. Since this technology is the basis of cryptocurrency, it is important to understand what Blockchain is and how it works.
If you are new to the world of cryptocurrency and investing in digital currencies, follow this article from Follow Technologies Magazine as we answer the question of what Blockchain is, explain its components and how it works, examine its advantages and disadvantages, and compare it to Bitcoin and traditional banks. Finally, we will explore predictions about the future of Blockchain technology, considering its features and functions.
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a network that uses decentralized and cryptographic technologies to store the history of all transactions made with digital assets such as Bitcoin in a digital and public ledger. The information stored in the Blockchain cannot be changed, and all information recorded in it is transparently available to users. The blockchain network makes it possible to remove banks and financial institutions from digital asset transactions. It ensures the security of digital currencies, a topic that has made digital assets gain many fans.
Blockchains are best known for their critical role in cryptocurrency systems in maintaining a secure, decentralized record of transactions. Still, their use cases are not limited to cryptocurrencies. Blockchains can be used to make data immutable across any industry. They can be used to create decentralized applications (DApps), supply chain management systems, voting systems, and more. Blockchain technology has the potential to transform a variety of industries by creating trust, security, and efficiency.
Since the introduction of Bitcoin in 2009, the use of Blockchain has increased through the creation of various cryptocurrencies, the emergence of DeFi, non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and smart contracts.
The definition of Blockchain is as follows: Blockchain technology is a structure that stores transaction records (blocks) in the form of a database called a “chain” in a network of “nodes” that are connected to each other in a peer-to-peer manner. The entire set is called a “digital ledger.” The concepts explained so far may seem complicated. Therefore, let us provide a simpler explanation of Blockchain.
Blockchain, in simple terms
To put it simply, Blockchain is a long chain of data. The data consists of transactions that occur on the network. The records of transactions are stored in packages called blocks. Each block is added to the end of the chain after its information is completed and verified. This chain of blocks, called Blockchain, is stored in the nodes of the network. Nodes are computers that store all the information on the network and store a copy of all the data.
What is a Digital Ledger?
Blockchain is a large digital ledger in which network transaction information is stored in a precise manner. Any information must be verified by a digital signature in order to enter the network and be verified by other network members. No one owns a blockchain network, and everyone can access all the information recorded in the network. Still, they cannot make any changes to the information. Because all the network information is stored in each node, all the copies available in all nodes must be changed to change it. In addition, the structure of the Blockchain is such that changing the information in a block will invalidate it.
Below, we will learn more about blockchain technology and, with examples, explain why buying Tether has more fans today than directly trading dollars between individuals.
An example to learn more about Blockchain
Suppose you want to transfer money through a bank network. The bank checks your account and the destination, transfers the money, collects its fees, and updates the balances of the source and destination accounts. But all of this is done by a system that the bank controls. If someone hacks into the banking system, they can transfer the money to their own account instead of your friend’s account. It’s interesting to know that this happens thousands of times a year around the world!
In the blockchain system, however, everything is transparent; your information and your friend’s information are checked and verified not only by a central entity like a bank but also by everyone on the network. Algorithms, hashes, and miners (you will learn more about these terms later) ensure that your digital assets are transferred correctly. After a transaction is completed, no one has the power to change the information related to it, and everyone on the network can see the transaction information. On the other hand, transaction fees are often much lower than bank fees. The issue of transaction fees becomes more important when moving large amounts of money.
History of Blockchain
Blockchain technology was first introduced in 1991 and has been evolving ever since. The following is a brief overview of the most important years in its development.
Blockchain technology in 1991
Introduction of blockchain technology by two scientists named Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta.
2000
Stephen Kent published his ideas and theories regarding cryptographically secure chains, along with suggestions for their implementation.
2004
Computer scientist and cryptographer Hal Finney introduced a system for digital cash called Reusable Proof of Work.
2008
An unknown person or group using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto proposed the concept of a distributed blockchain, also known as a Peer-to-Peer Distributed Timestamp Server, in the Bitcoin White Paper.
2009
Satoshi Nakamoto launched the first Blockchain as a public ledger for transactions made using Bitcoin.
Blockchain in 2014
The idea of Blockchain 2.0 was conceived with the aim of using this technology’s potential in areas beyond decentralized value transfer. Blockchain 2.0 sought to enable the use of Blockchain for the development of decentralized businesses and organizations using smart contracts, which in the future led to the formation of an important field called DeFi.
2015
Launch of the Ethereum Frontier network, the first public version of the Ethereum blockchain that allowed developers to create smart contracts and decentralized applications.
2017
Japan recognized Bitcoin as a legal tender. Block. One designed the EOS blockchain operating system to support decentralized commerce applications.
2018
Bitcoin turned 10 years old in 2018, and its price fluctuated between $4,000 and $16,000 this year.
2019
The number of daily transactions on the Ethereum network reached more than 1 million transactions.
2020
Stablecoins gained traction, and Ethereum launched Beacon Chain in preparation for Ethereum 2.0, a proof-of-stake version of the network.
2022
The consensus mechanism on the Ethereum network changed from the old and expensive Proof of Work (PoW) model to Proof of Stake (PoS). In the process, the Ethereum mainnet merged with the Beacon Chain.
This section only introduces some of the most important annual changes related to the blockchain space. It should be noted that blockchain technology is still evolving, and there have been many developments in this area over the past few years, which would require a longer article to mention.
What components does the Blockchain consist of?
Blockchain consists of three basic and important concepts:
- Blocks
- Miners
- Nodes
We will examine each of these concepts below.
What is a block?
The packets of information in the blockchain network are called blocks. Each network is made up of a large number of blocks, and each block consists of three basic parts:
Data
Block information, which includes transactions made in the block.
Nonce
A nonce or one-time number in the Blockchain is a 32-bit number (a number with 2 to the power of 32 or 4 billion different combinations) that is randomly generated when a block is created and then used as a hash header in the block.
Hash
Hashes are 256-bit numbers that are placed next to a nonce. Miners’ job is to find the correct nonce, which can be used to arrive at a valid hash of a block.
What is a miner, and what is its role in the Blockchain?
Miners are responsible for creating blocks in the network, a process called mining. In the blockchain network, each block has its nonce and hash. In addition, the hash of the previous block is also stored in the new block. Therefore, mining or creating a block is not a simple task, especially in a large network where millions of blocks are stored. Miners use powerful software and hardware to solve complex mathematical problems and create a nonce that can accept the hash.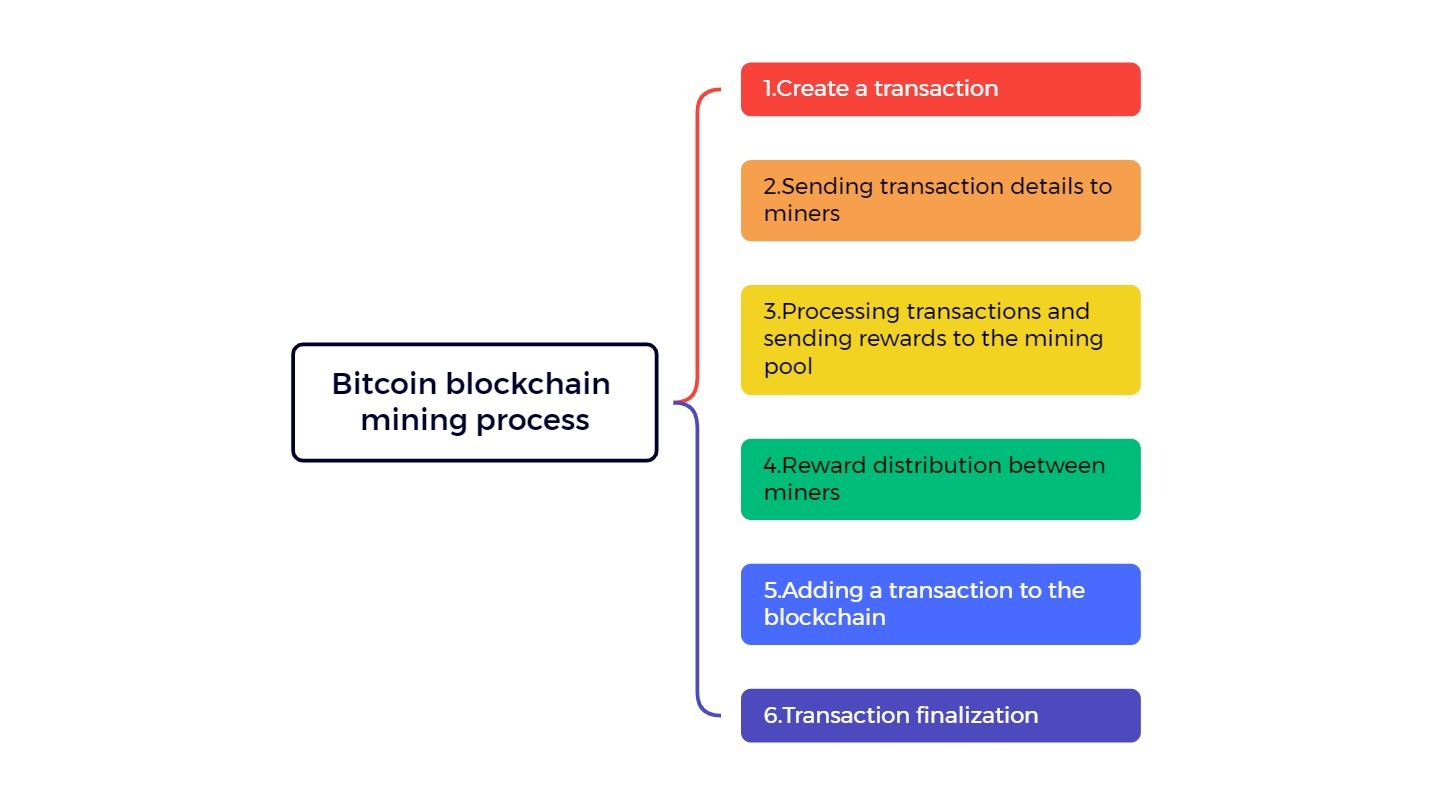
Why does the mining process require so much energy?
As we mentioned, the nonce is 32 bits. While hashes are generated in 256 bits, connecting a 32-bit nonce to a 256-bit hash is a very complex task, requiring billions of different calculations before miners can finally find the right combination. Once the right nonce is found, the block is ready to be added to the network. When the block is successfully added to the network, all nodes in the network confirm it, and the miner receives a network reward (such as Bitcoin) for their efforts.
This entire operation is called Proof of Work, which ensures that everyone on the network is sure that the block information is correct. Miners can earn a good income and earn Bitcoins in this way. The payment of Bitcoins as a reward provides the necessary incentive to perform these calculations on blockchain networks.
What is a node in Blockchain?
A node is any electronic device that can store a copy of the entire network and enable blockchain activity. Nodes implement decentralization of processes and information distribution in Blockchain.
The nodes verify each new block that enters the network. Blockchain’s transparency allows all its information to be easily checked and viewed. This transparency is due to the presence of nodes. All nodes are connected in a peer-to-peer manner, which allows them to store the same information. Storing information using a strong control system helps maintain the integrity of the network and will create trust among users.
The difference between a node and a miner
In the Bitcoin network, all miners are nodes and have a complete copy of the transaction history. However, not all nodes are miners and may not play any role in generating new blocks; that is, they do not dedicate the processing power of their computer systems to mining blocks and verifying user transactions.
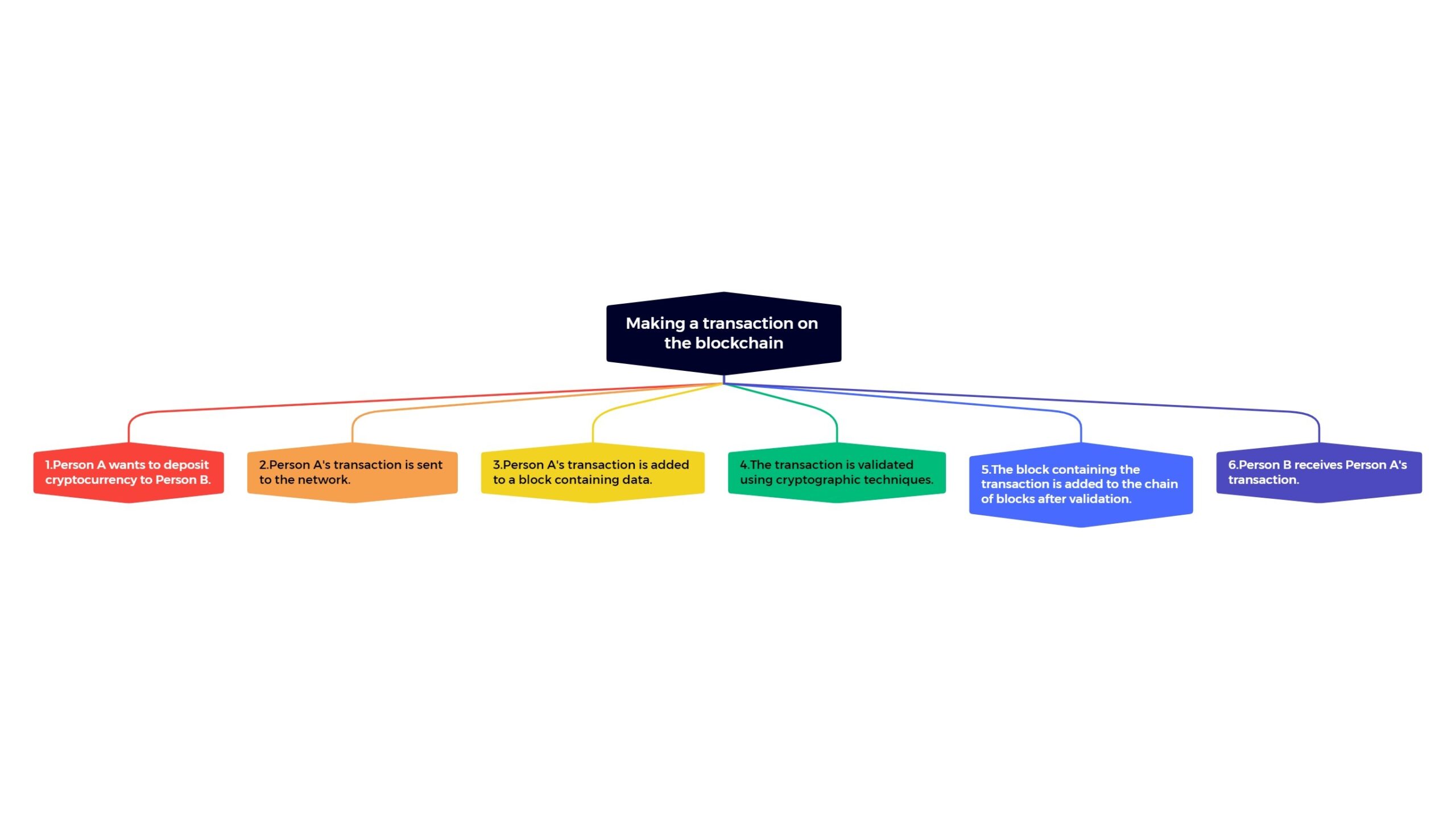
How does Blockchain work?
In the previous section, you learned about the components of a blockchain, and now it’s easier to explain the process of making a transaction on a blockchain. Transactions follow a specific process depending on the Blockchain they’re made on. In the Bitcoin blockchain, your transaction is sent to a memory pool called the mempool, where it’s stored and queued until a miner or validator receives it. A Bitcoin miner then selects your transaction and adds it to a block. A block is a space where transactions that users have requested to be processed are kept.
The miner’s job is to prove the work done on the network by performing a series of complex mathematical calculations and guessing the hash number. The block containing your transaction is then confirmed on the network and added to the chain of previously confirmed blocks. In addition, each block created after the block containing your transaction is considered a new confirmation of your transaction.
It should be noted that the process described applies to the Bitcoin network. Still, the Ethereum, Solana, or other blockchains may follow a different method for completing transactions.
How is Blockchain secured?
Blockchain uses several layers of security, such as different algorithms, Proof of Work, hashes, Peer-to-Peer systems, etc., which together create a very secure and stable network. New blocks are always added to the end of the Blockchain, and this makes it impossible to change previous blocks. Also, the hash alone can provide security for an entire chain of blocks. Each block contains the hash of the last block, and a change in any data changes the hash of the block in which it is located. Other layers of blockchain security include private keys and public keys, which we will learn about later.
What is a private key?
A private key is a code consisting of numbers and letters that is randomly generated and given in secret to someone who sets up a new wallet or address on the Bitcoin network. The wallet owner actually uses this private key to control their address and can sign a transaction or send some of their assets to another address. The recovery phrase or 12-word password of digital wallets is also created using the private key. It is actually a simpler version of the private key provided to the user. Note that protecting and keeping the private key, as well as the recovery phase, is essential to maintaining the security of blockchain wallets.
What is a public key?
The public key is also a code consisting of numbers and letters that are created using a cryptographic algorithm from the private key. Then, using a similar algorithm, the wallet address is made from the public key. As you can see, the private key, public key, and address of each wallet are related. Still, the advanced encryption system in blockchain networks is designed in such a way that it is practically impossible to guess and reach the private key from the address or public key. This ensures the security of wallets in blockchain networks.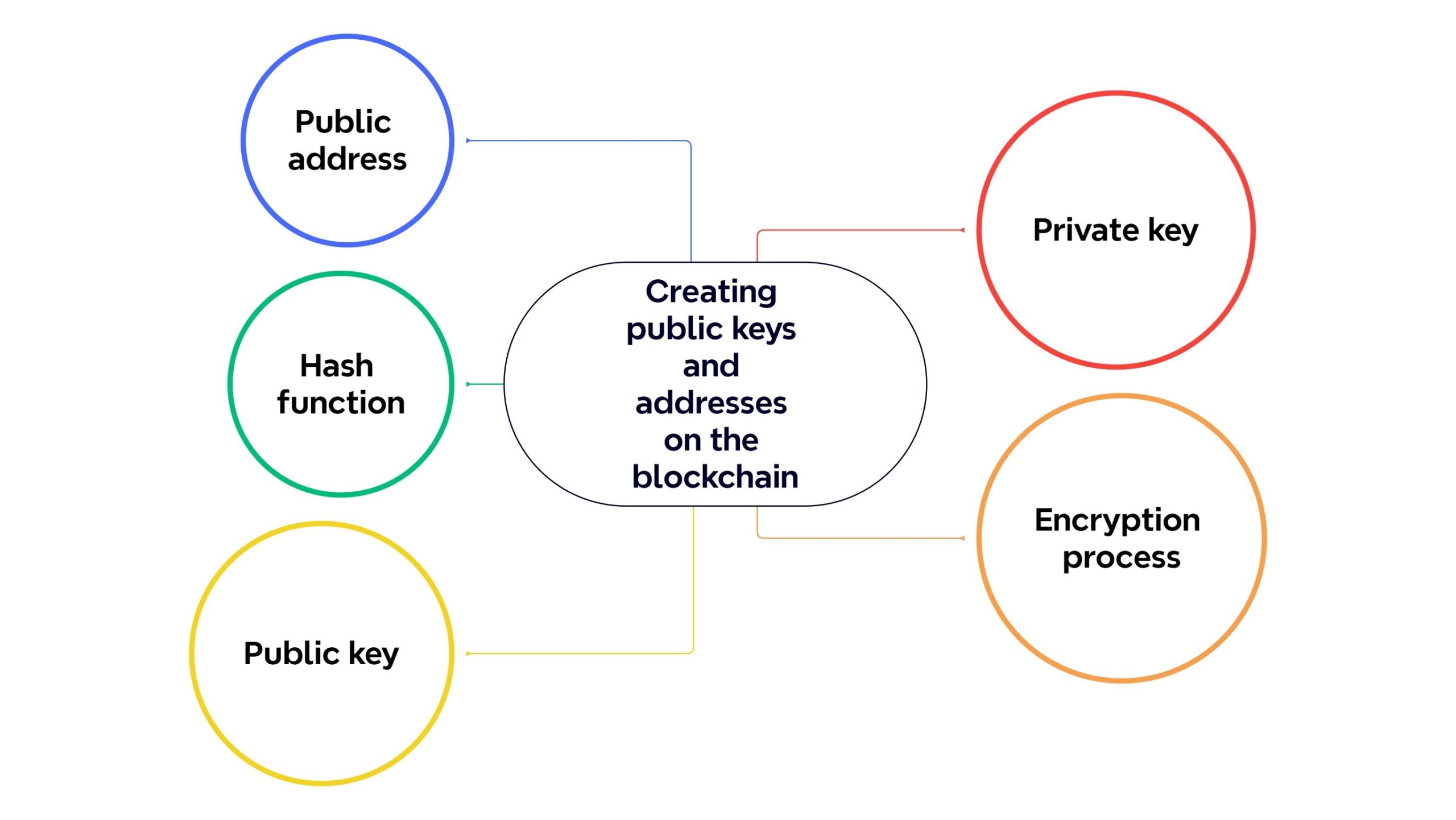
The difference between Blockchain and Bitcoin
Although Blockchain and Bitcoin are two closely related concepts, it should be noted that they are not the same and have some differences. In fact, Blockchain, as mentioned earlier, is a technology for developing a decentralized and distributed ledger that enables transparent, secure transactions and data storage. Bitcoin, however, is a blockchain network and, of course, the digital currency of the same name that is transferred on this network. There are other blockchains other than Bitcoin, some of which you may have heard of, such as Ethereum. These blockchains may have different designs and capabilities than the Bitcoin network.
In short, Blockchain is the underlying technology that powers Bitcoin and many other cryptocurrencies. At the same time, Bitcoin is a specific cryptocurrency on its own Blockchain.
| Feature | Blockchain | Bitcoin |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A technology for building a digital, distributed ledger. | A blockchain network and digital currency |
| Used | Finance, computer games, logistics, supply chain, healthcare, and other areas. | Transfer of value and payment |
| Basic technology | Blockchain is based on cryptographic technology and uses the concept of distribution and creating a network of coordination between people. | Blockchain |
| Security | Blockchain provides high security in transactions due to its use of strong and distributed cryptographic algorithms. | Bitcoin also provides high security in transactions due to the use of strong cryptographic algorithms and the distributed blockchain system. |
Comparing Blockchain with the Traditional Banking System
There are several major problems that you face when working with the traditional banking system. When you are sending money to others, the banking system deducts a significant fee from your account. The system has access to all account information and can change all accounts. The centralization of the system means that if the information in the bank is lost, all account information will be lost, too. Finally, banking systems control money transfers.
Blockchain has many advantages over a traditional banking system, some of which are mentioned below.
- Possibility of conducting transactions anonymously
- Pay a small fee
- Distributed and nearly unhackable system
- Transparency
- No need for intermediaries
- Very high network security
- Immutability of information
- Sustainability
- Lack of a central controlling entity
- Ability to move assets regardless of geographical location
- High transaction speed
To better understand the differences between a bank and a blockchain, we have compared the banking system and the Bitcoin blockchain in the table below.
| Feature | Bitcoin blockchain | Banks |
|---|---|---|
| Working hours | 24 hours a day, every day of the year | All banks are closed on weekends and public holidays. |
| Transaction speed | Bitcoin transactions can take as little as 15 minutes to as long as an hour, depending on network congestion (this time is much less on other networks). | Bank transfers are not usually processed on weekends or bank holidays. |
| Ease of transportation | Internet and mobile phone connection are the minimum requirements. | An ID card, bank account, and mobile phone are the minimum requirements for digital transfer. |
| Privacy | If Bitcoin is purchased anonymously, it is impossible to determine who owns it. | Bank account privacy is limited by how secure the bank's servers are and how well each user protects their information. |
| Security | The larger the Bitcoin network becomes, the more secure it becomes. | Bank account information is only as secure as the security of the bank's server that contains the customer's account information. |
Applications of blockchain technology
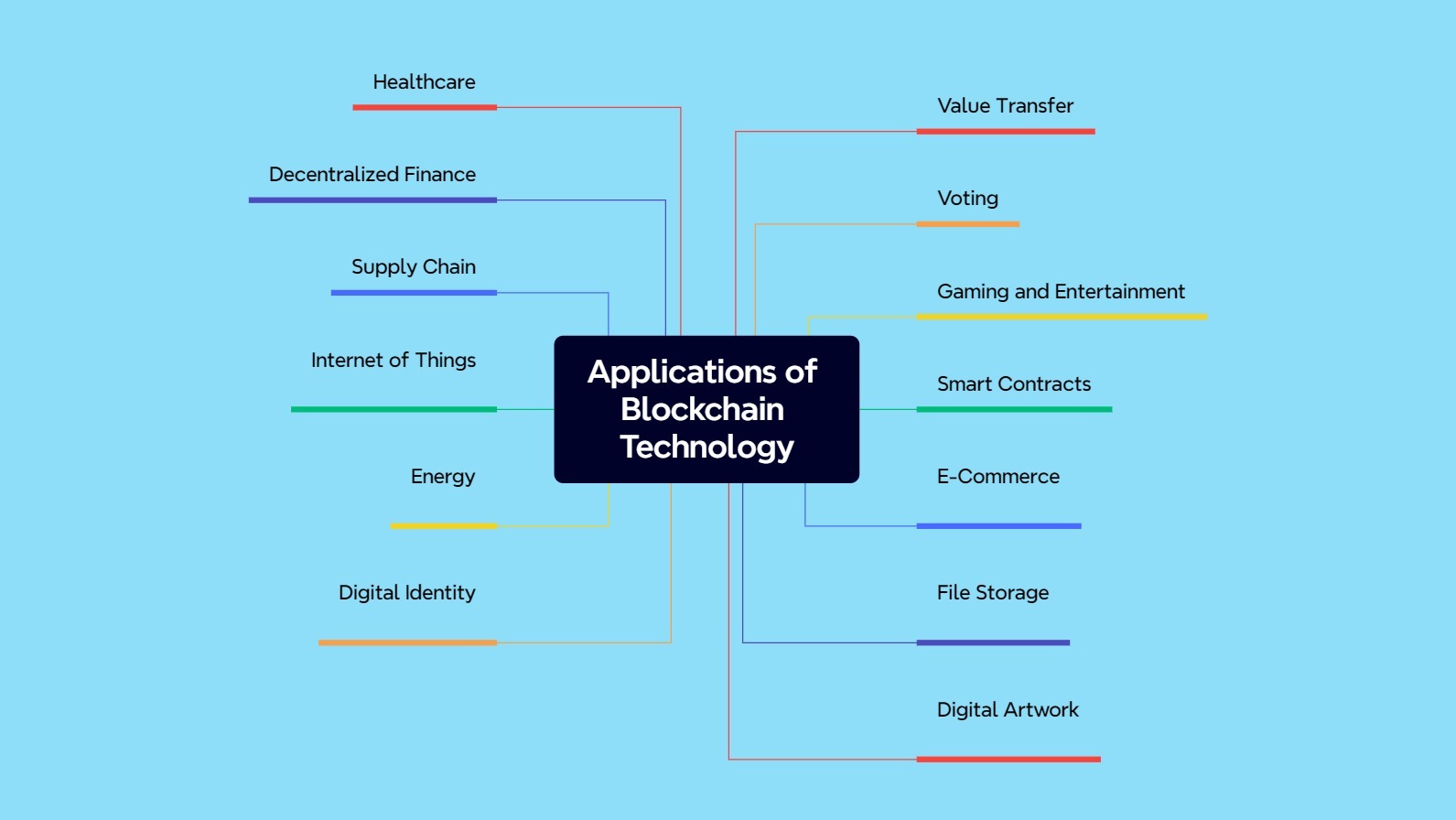
Blockchain has many capabilities, of which asset transfer is just one. Over the past few years, a variety of ideas have been proposed in the field of Blockchain, making the technology more applicable than ever before. Below, we will learn about some of its applications.
Value transfer
As mentioned, value transfer is one of the most fundamental uses of Blockchain. Us Blockchainhain networks like Bitcoin, a valuable entity, BTC, can be moved between different addresses without geographical restrictions and regardless of the transaction value. Value transfer in blockchain networks is done quickly and at a very low cost, and the identity of the receiver and sender of the assets remains largely anonymous.
Smart contracts
Smart contracts are software that automatically performs certain tasks under specific and predetermined conditions. Blockchain networks are the platform for implementing and developing smart contracts. Many well-known platforms in the cryptocurrency space, such as decentralized exchanges (DEX), NFT marketplaces, or decentralized social networks, now have millions of users using smart contracts.
Defi or Decentralized Finance
DeFi platforms are applications that decentralizedly provide cryptocurrency users with services similar to real-world financial services. Lending, asset exchange, cryptocurrency insurance, and staking are among the most widely used services offered in the DeFi space and have engaged many users.
Internet of Things
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of electronic devices that are connected to the Internet and exchange information. Connecting these devices to the Internet allows them to be controlled and managed using dedicated software. For example, you can connect to your home’s cooling system with software on your mobile phone and program it to bring the room temperature to your desired level before you arrive home.
Blockchain can be a good option for developing the infrastructure needed to manage IoT-based systems. In cases where the issue of payment and the need to conduct transactions or record payment records to use IoT systems arises, Blockchain can again come to the aid of this technology.
Digital identity
A digital identity management system implemented using Blockchain can be a secure infrastructure for storing personal identity information without the need to disclose individuals’ identities. In such a system, individuals largely own their own data, and user privacy is maintained at the highest level.
Information storage
Centralized cloud storage and providers such as Google Drive have many security weaknesses and vulnerabilities. Providing decentralized storage is one of the special applications of Blockchain. In Blockchaintems, people use the storage space of computer systems distributed around the world and, in return, can pay the maintenance fee with digital currency.
Digital artwork presentation
Creating non-fungible tokens, or NFTs, is one of the most popular uses of Blockchain, and it has grown exponentially in recent years. Using standards that exist on blockchain networks, people can turn their digital artwork into a token and value it for sale.
It is worth noting that blockchain technology has other proven and experimental applications that are increasing daily. This section only mentions some of the applications of Blockchain that are more prominent than others.
Blockchain Technology Layers
Blockchain is a combination of several different technologies, all of whose transactions are stored on a distributed ledger (DLT). The distributed ledger is responsible for adding and verifying each transaction on the network. Blockchain uses blockchain design to support this authentication method. The 5 blockchain layers involved are:
- Hardware infrastructure layer (Infrastructure layer)
- Data layer
- Network layer
- Consensus layer
- Application layer
Each of these layers has its own purpose and function, which we will briefly introduce below.
Hardware infrastructure layer (Infrastructure layer)
The infrastructure layer is the most fundamental layer of the Blockchain; it processes and stores transactions with its nodes. The main purpose of this layer is to keep the distributed ledger of the blockchain tamper-proof by validating and storing blockchain transactions in a decentralized manner. By creating a distributed database, all data is stored transparently in the Blockchain. Transactions and data stored in the blockchain infrastructure layer are verified through consensus mechanisms.
Data layer
The second layer of the blockchain is the data layer, which ensures that all blockchain transactions are transparent, immutable, and undeletable once added. This layer is where blockchain transactions are stored on the distributed ledger.
Network layer
The network layer, also known as the P2P layer, is responsible for connecting all the nodes of the blockchain network and transmitting messages that help validate transactions and blocks before they are added to the Blockchain.
Consensus layer
The consensus layer, the fourth layer of the Blockchain, is the blockchain validity of blockchain transactions. It allows nodes to agree on the order of blockchain transactions using various algorithms, including Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), and Operational Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT).
Application layer
The last layer of the blockchain is the application layer, and it is through this layer that users interact with the blockchain technology. Smart contracts and decentralized applications reside in this layer. Without this layer, the blockchain is nothing more than a distributed database.
Benefits of Blockchain
So far, a significant portion of the benefits of blockchain networks have been mentioned. Below, we will explain the benefits of blockchain in more detail so that you can become more familiar with this technology.
Accuracy of the Chain
Transactions on the blockchain network are verified by thousands of computers and devices, ensuring an accurate record of information. Even if a computer on the network makes a calculation error, the error is only made to one copy of the blockchain and is not accepted by the rest of the network.
Cost Reductions
Blockchain eliminates the need for third-party verification and the associated costs. In contrast, in decentralized networks like Bitcoin, there is no central authority, and transaction fees are capped.
Decentralization
The blockchain does not store any of its information in a central location. Whenever a new block is added to the blockchain, every computer on the network updates its blockchain data to reflect the change. This makes it more difficult to tamper with the blockchain.
Efficient Transactions
In some blockchains, transactions can be completed in minutes and are guaranteed to be secure within minutes. Using blockchain technology, you can easily buy and sell different cryptocurrencies. This feature is especially important for cross-border transactions that are limited in the traditional sector.
Private Transactions
With an internet connection, you can view a list of network transactions on many blockchain networks. The important thing to note is that although transaction details are visible, the identifying information of the users who made the transactions is not visible, and your transactions are private.
Secure Transactions
Transactions on the blockchain network are completely secure because after each transaction is recorded, the authenticity of this transaction must be verified by the blockchain network. After verification by the network, the transaction is added to the Blockchain.
Transparency
Transparency is an important feature of blockchain technology because most blockchains are open source, meaning that all users can view the code. The open-source nature of blockchain code means that there is no single point of control or editing, and anyone can suggest changes or improvements to the system.
Expanding access to financial services (Banking the Unbanked)
One of the important features of Blockchain is That It Can be used by anyone around the world, including the unbanked. This feature allows many users to store their assets in digital currency instead of keeping them in cash or in banks, reducing the risk of their assets being stolen.
Disadvantages of Blockchain
Blockchain has many applications and advantages, but like any other technology, it faces limitations in some areas. Below, we review some examples of limitations related to blockchain technology.
Technology Cost
Although blockchain can save users on transaction fees, the technology is not free. For example, the Bitcoin network’s proof-of-work system uses a huge amount of computing power to validate transactions. In the real world, the total energy consumed by the vast number of devices on the Bitcoin network is more than the annual electricity consumption of countries like Norway.
Speed and Data Inefficiency
Bitcoin is a great case study for the potential inefficiencies of blockchains. Bitcoin’s PoW system takes about 10 minutes to add a new block to the blockchain. At this rate, it is estimated that the Bitcoin blockchain network can only handle about 7 transactions per second (TPS). Although other networks like Ethereum or Solana perform better than Bitcoin, they are still limited by the blockchain. Another issue is that each block can only hold a limited amount of data. The block size issue is one of the most challenging issues for the scalability of blockchains in the future.
Illegal Activity
Confidentiality, a positive feature of blockchain technology, protects users’ privacy and prevents hacking. However, it also allows for illegal trade and activity. With the help of blockchain technology, people can buy and sell illicit goods on the dark web and transfer money using digital currencies.
The challenge of regulation
The lack of clear rules and regulations regarding blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies is a concern for users. Some governments may declare the ownership and transfer of money in cryptocurrencies illegal, which would harm users. However, with the increasing acceptance of cryptocurrencies in recent years, this concern has decreased, and many platforms have allowed their users to make payments in cryptocurrencies.
51% attack risk
In blockchain networks such as Bitcoin, if a group of nodes or miners manage to control more than 50% of the hash rate or processing power of the network, they will be able to sabotage the network and change some data, for example, preventing the processing of some transactions or reversing a confirmed transaction.
Reversing a transaction exposes the network to a risk called double-spending, a situation in which a malicious person is able to spend a given cryptocurrency more than once. The proof-of-work consensus algorithm in blockchains is designed to combat this problem, and the likelihood of such disruptions occurring in secure and distributed blockchain networks such as Bitcoin is very low. However, a 51% attack is one of the risks that blockchain networks face.
Types of Blockchain
There are different types of blockchain technology, each with its unique characteristics. The 4 types of Blockchains are:
Public Blockchains
Public blockchains allow anyone to join the network, verify transactions, and develop smart contracts. Two well-known examples are Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Private Blockchains
Private blockchains are networks created by organizations or businesses for specific purposes. These blockchains are often not decentralized and are controlled by a central entity.
Hybrid Blockchains
Hybrid blockchains combine features of public and private blockchains. They allow organizations to control who can access the data stored on the Blockchain, and the blockchain is publicly available.
Consortium Blockchains
A consortium blockchain, also known as a federated blockchain, is a private blockchain with access restricted to a specific group. This eliminates the risks associated with a single entity controlling the network in a private blockchain. In a consortium blockchain, consensus procedures are controlled by predetermined nodes.
The four types introduced are just some of the main types of Blockchain. With the increasing advancement of blockchain technology, the possibility of new types and variations is not out of the question.
Blockchain algorithms and mechanisms
Blockchain algorithms are an important part of this technology, which records and verifies transactions across multiple nodes. Below, we will briefly introduce some important blockchain algorithms.
Hashing Algorithms
Blockchain algorithms often use hash functions to create digital signatures. Two popular hash algorithms are SHA-256 and Keccak-256.
Proof-of-work algorithm
Proof of Work (PoW) is a consensus algorithm used in many blockchain networks, including Bitcoin. In short, the first miner to correctly perform the calculations required to mine a block adds a new block to the Blockchain. The blockchain-work consensus algorithm ensures network security, but it also requires significant energy.
Proof of shares
Proof of Stake, or PoS, is a consensus algorithm that selects validators to create new blocks based on the amount of cryptocurrency they are willing to lock up as a stake. Since the Merge update, Ethereum has become an example of a proof-of-stake blockchain.
Algorithm for Proof of Stake Transferred
Delegated Proof of Stake, or DPoS, is an HSJ consensus algorithm used by the Tron and EOS blockchains. It aims to achieve higher throughput than Proof of Work and Proof of Stake.
Operational Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) algorithm
Operational Byzantine Fault Tolerance, or PBFT, is a consensus algorithm designed primarily for private blockchains. It allows the network to function properly even if some nodes are down.
Directed Acyclic Graph Algorithm (DAG)
Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAG) is a technology for developing a distributed ledger that is structurally different from blockchain. Instead of blocks, DAG uses nodes to represent the relationship between transactions, and each transaction confirms the two previous transactions.
The introduced algorithms are just a few of the blockchain algorithms. Different blockchains may use different algorithms and consensus mechanisms depending on their specific goals.
The Future of Blockchain
In Professor Klaus Schwab’s book “The Fourth Industrial Revolution”, the keyword blockchain is mentioned as the engineering technology of the future of humanity. Considering current trends, it is predicted that blockchain will bring about major changes in many industries in the coming decades. Some important areas that are likely to witness major changes using blockchain technology in the future are:
Cybersecurity
Given that it is a distributed system, blockchain technology can prevent tampering, secure data, and allow users to verify the authenticity of files.
Government
Governments can use blockchain technology to replace traditional paper-based systems. Using this technology for voting also reduces the possibility of fraud and helps protect voters’ identities.
Finance and Banking
Given global inflation and the rising costs of transferring money between financial intermediaries, developing countries are expected to turn increasingly to cryptocurrencies. One promising area for blockchain development is the creation of national cryptocurrencies that address the shortcomings of existing traditional currencies.
Medicine
Blockchain can be used to develop applications for managing patient data, controlling drug supply, and automating medical examinations and healthcare transactions. It will also be an effective tool for verifying the authenticity of vaccine shipments and tracking vaccine distribution, alleviating concerns about the production and distribution of counterfeit vaccines.
Marketing
Blockchain will be a very useful and applicable technology in the field of marketing in the future. Using blockchain will increase the monitoring and measurement of the effectiveness of advertising campaigns and minimize cases of advertising fraud. Blockchain can also help collect data on customer behavior and psychology.
Conclusion
In this article, we learned about the concept of blockchain, its components and how it works, its advantages and disadvantages, the types of blockchain technologies, and how it differs from the digital currency Bitcoin and traditional banks. Blockchain is a decentralized network that allows transactions to be carried out securely, and data transparency and user privacy confidentiality help it gain wider acceptance.
Although this technology is known for digital currencies, especially Bitcoin, its uses are not limited to the crypto world. As we enter the third decade of blockchain, its uses are also expanding. By creating an account on the online exchange Nobitex, you can experience some of the amazing benefits of blockchain technology and buy digital currency quickly and securely.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between Blockchain and Bitcoin?
Blockchain is a technology that develops a distributed ledger. At the same time, Bitcoin is a blockchain network, and the digital currency is built on it.
Which is the best Blockchain?
Bitcoin, Ethereum, Solana, Binance Smart Chain, Cardano, Avalanche, and Tron are some of the most popular blockchain networks, each with its specific uses.
How to build a blockchain?
Building a blockchain that is efficient and sustainable requires mastery of programming languages and concepts related to blockchain networks.
Which is the fastest Blockchain?
Solana, The Open Network, Fantom, and Algorand are some blockchains that are known for their high transaction processing speed.
What is the largest Blockchain?
The Ethereum network is the largest blockchain, with tens of billions of dollars in locked assets and hosting a huge number of protocols, tokens, or NFTs.








The content is great. But it doesn’t cover the fundamental questions. For example, when a miner receives a reward, what exactly is the problem being solved? What system or person is generating these problems? Why can’t we solve the problems randomly and earn Bitcoin? No matter how much I read about blockchain on different sites, I couldn’t figure this out.
Hello
Good time
Thank you for sharing your opinion with us. It is really not possible to answer these questions in the form of a comment. In short, if we want to mention it as a headline:
Miners actually use their processing power to try numbers one after another to get the answer to the equation of each block (hash function) and in return for doing this, they receive a reward in the network.
So the more processing power a miner has, the better their chances of discovering the hashed numbers (like solving a puzzle).
But this is the old form of mining. Today, miners connect to mining pools and connect their power with a network of miners. In the end, the reward is distributed among all miners in the pool (based on the power of each miner).
In addition to this, the concept of mining difficulty should also be considered, which does not automatically allow a miner to mine a block earlier than 10 minutes.
Thank you for your support
Hello. Do I have permission to use this article for a class presentation?
Hello. Yes, with honor.